- 有关1.11版本前的后勤系统,请参考本页面的历史版本。
在钢铁雄心4中,后勤(Logistics)是指将战斗人员(增援)和装备送到需要的地方去,以此来支持作战部队,同时确保作战单位所在地的补给水平足够他们有效率的行动。其中最重要、最复杂的元素就是在1.11版本(“巴巴罗萨”补丁)大改的补给系统。
补给
|
|
这部分内容可能已不适合当前版本,最后更新于1.11。 |
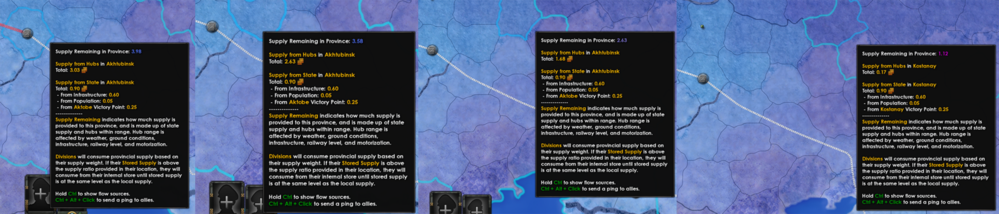
补给本身并不是生产出来的,省份的补给水平代表了对作战部队的“支持限度”(可以把它看成是一种柔和的单位堆叠限制)。每一个陆战单位自身也有一个内部的补给状态,和其所在省份的补给水平相独立,但两者之间也有关连。
一个省份的可用补给来源于三个不同的部分:“补给中心补给(Hub Supply)”、“空投补给(Aerial Supply)”和“地区补给(State Supply)”。补给中心的补给是通过补给网络从一个国家的首都运输到此国前线作战部队的。而补给网络则由补给中心、港口、铁路和运输航线构成。空投补给是由执行空投任务的运输机提供的,仅对其空投的空域有效。地区补给则是指每个地区都有的一个固定的补给量,所有作战单位都可以从所在地区中获得补给(如果是一个还没有被某一方所完全占领的地区,该地区的补给则由占领的数方部队共享)。
- 值得注意的是,即使一个作战单位能从补给中心获得所需的全部补给,他依然会从所在地区的补给当中抽取一部分。实际上,他们会优先使用地区补给,其次使用补给中心的补给,最后才使用空投的补给。
只要作战单位所需的补给总量小于所在省份能提供的补给量,那么这些作战单位就能完全补给。相反,则这些作战单位将承受惩罚。下面将会详细介绍。
补给地图
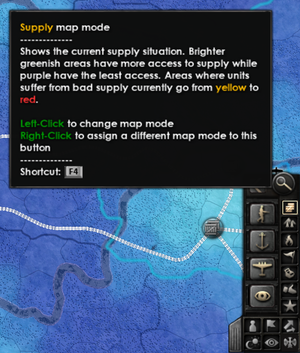
补给情况在游戏中主要通过供应地图模式显示。在默认设置下,可以通过按下"F4"键或在屏幕右下角选择补给地图模式图标来访问此模式。
补给地图通过不同的着色来展示每个省份的供应状况。这些颜色渐变使得同时查看数百个省份的补给情况时也能一目了然。
- 亮(浅)蓝色:有大量可用的补给
- 深蓝色:有少量可用的补给
- 紫色:有少量或没有可用的补给,但该省份的部队没有受到低补给的影响。
- 黄色:该省份的部队补给供应部分不足,但仍有足够的补给让部队不至于受到严重的debuff。
- 亮红色:该省份的部队补给供应严重不足,它们正遭受重大的补给相关惩罚。
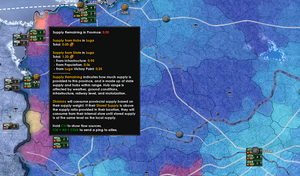
The tooltips in the supply mapmode are invaluable, and hovering over different items shows different information:
- Unit: Unit supply draw, and where it’s coming from.
- Supply hub: Amount of supply requested of the hub, and highlights the railroad connection to the capital. Holding down the Shift key will show the range of the supply hub (at that time – range can change with weather).
- Port: Amount of supply requested of the hub, and shows paths to any ships that may be drawing Hub (but not State) supplies from the port. Holding down the Shift key will show the range of the supply hub (at that time – range can change with weather).
- Province: Total and available supply in a province. Holding down the CTRL key will also show a breakdown of where the hub supply is coming from.
后勤
补给中心
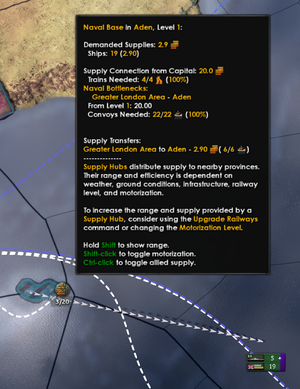
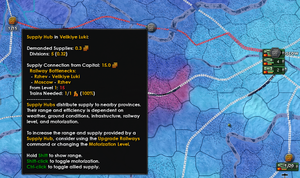
中心补给是给补给中心或者港口提供补给 (激活的补给中心, 港口也一样),我们关注中心补给时有3个要素需要注意:
- 一个补给中心的可消耗的总容量。
- 补给中心的范围,和一个特定省份补给中心补给量。
- 一个特定省份收到的补给来源于所有范围中的补给中心。
大多数情况下,在写文本时,最常见的供应问题是基于特定省份的不充足的供应,不是总供应量不足。
总补给中心补给能力
补给中心/港口的总吞吐量基于与首都相连不同等级的铁路相连的补给中心/港口,首都之间,港口之间的铁路水平(包括车队的到达和离开)
与首都相连的一个补给中心的一级铁路为该补给中心提供了一个基本15的供应吞吐量,每个增加等级铁路建筑吞吐量增加5,直到最大值35。等级1的港口与其他等级的港口供应,收到的港口基础是8补给。每个增加的港口等级建筑会增加3的补给吞吐量,直到最大35。注意:如果护送车队供应中的港口被袭击,供应提供量会被减少直到铁路被恢复其容量,此外,供应生产量的上限基于最小的铁路或港口供应量在任何一个相连的店(所以,举个例子,如果有3个铁轨,2个等级2,1个等级1,相连被认为是一个1级相连同时有15的补给,直到升级到等级2相连会有20的补给量,等级1的铁路会需要升级到等级2)(另一个例如,如果有3个铁路相连到等级6的港口到一个等级5的港口,链接被认为是一个等级5的相连并提供20的供应)。河流可用作一级铁路连接。
每级港口提供的补给量
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 20 | 23 | 26 | 29 | 32 | 35 |
每级铁路补给量
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 |
一个例外是这个首都的补给中心,它的吞吐量基础是5,然后一定量的民用工厂和军用工厂和造船所。
补给中心供应范围
补给中心供应给每个身份基于许多因素,最重要的是省份之间提供存在的补给中心,这个存在的修正主要是铁路连接的等级去供应来自首都的补给中心,基础设施(指所有可以建筑)的水平。
提升补给范围
除了空中补给以外,给一个省份提升补给水平是在整个游戏的过程中,几乎总会完全的由于改善了补给中心的供应量。下列4个方法可以提升。:
- 增加补给中心的机动化水平或是军队的(军队的补给机械化指令)
- 增加铁路链接到补给中心的等级。
- 增加地区的基础设施等级。
- 建造一个新的补给中心
注意,前三种方法(机械化,增加铁路连接等级和增加基建等级)总是可以叠加-所以一个摩托化补给中心是一个地区有1级基础建设和1级的铁路相连将会有最小的供应范围,当一个完全的摩托化补给中心和5级基建和5级铁路相连,会有最大的补给范围。
非常重要的一点是关心补给中心供应,分散开来可以显著的增加,特别是来自更多的补给中心和港口,或首都-------增加补给范围,分别建设的改变也许相对较小,经常投入大量的投资可以增加范围也许会足够推进他从中心到下一个省份。
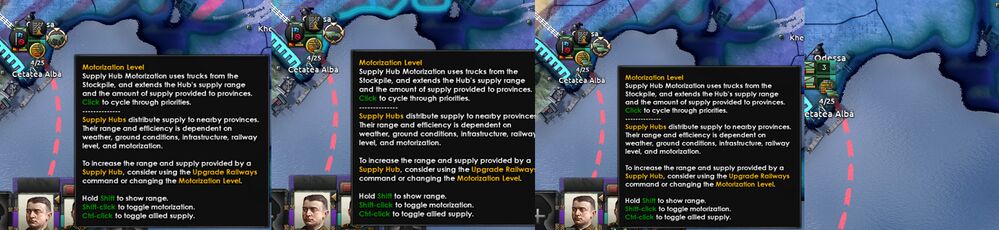
摩托化
默认情况下,每个补给中心设置成非摩托化,图片是一个马。这是个可以提升到2个不同的摩托车,单击可以让他变成运转图标(看举例的图片)。一旦一个中心摩托化后,图标会变成1个或者2个小卡车(基于于摩托化水平),一个绿色或者更多的卡车表示,这个补给中心直接描述的摩托化,当灰色卡车表示,它已经变成摩托化并支援了附近的军队---更多的在下面。注意补给中心变成卡车赋值摩托化,无论是否直接的经由补给中心或选择摩托化,选项,都不会消耗燃料或人力。
依赖于摩托化的等级,每个补给中心需要0,40,或80的卡车(图片为,马,1辆车,2辆车)
这些卡车损耗,在恶劣的 地形和天气下增加,它们也会受到来自敌人飞机的后勤打击任务
其他方式达到补给中心摩托化,在军队等级去分配它。这将自动切换在军队获取补给品的范围内的枢纽上为军队设置的机动化水平。这一优点是降低了枢纽机动化水平的微观管理,但它可能导致对军队的需求波动,因为军队范围内的枢纽数量随着时间的推移而变化。请查看下面的三个截图和说明
请注意,只有在有足够的卡车时,才会得到机动化的全部好处。如果分配给支持枢纽的卡车比可用的要多,那么收益将会减少,与卡车的短缺成比例。
提高铁路等级
在摩托化之后,增加铁路链接等级是下一个最有力和常见中最快的(但它取决于如何离你的首都和铁路供应补给中心有多远)
每个铁路花费170CIC,+130CIC给每个存在的铁路等级(最大到等级5),所以,它相对最快和最便宜去放置一个等级1的铁路,订单一个长的等级5的铁路是一系列的企业建设。举例说,详见下表,总CIC去建筑铁路来自没有到达5,是2.150CIC每个省份(170+300+430+560+690),修正后的任何建设奖励和基础建设速度影响。
| 铁路等级 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIC 花费 | 300 | 430 | 560 | 690 | 820 |
实际上铁路建筑可以有很多种方式:
- 选择补给中心,然后点击中间按钮(顶部)三个显示图标中间,每次点击会提升其他铁路等级到连接到首都的每个省份铁路的连接情况,3次补给连接可以让2级的铁路铺设命令到最大等级
- 开放生存可以让生产界面,和选择“铁路”按钮,然后点击白色按钮中的一个,在黑色圈一个由2个补给中心铁路连接-这会放置铁路建设命令去增加铁路等级在2个补给站中间,每次增加会放置铁路增进等级
每增加一级的铁路会增加补给中心一定大小的总补给供应,它意味着补给流动从补给中心外流也会增加。在一些情况下也意味着省份可以在没有贸易中心的情况下会收到一些补给中心的补给,如上所述,增加“供应流动下降”更远来自补给中心意味着补给扩张范围可能会受到限制。
请记住,铁路对战略重新部署也很有用,而且铁路水平越高,部队的战略重新部署速度就会越快。
建造新的补给中心
如果它看起来是没有成本收益,可能,需要建设一个新的补给中心来补给。在海岸上,港口作为供应枢纽,而且要便宜得多(海军基地第一级为5000CIC,后续每级的成本再增加1000CIC)。然而,内陆地区需要使用供应中心,这需要20000个CIC(由任何建设速度和基础设施建设奖励修改)。 港口和供应中心都是使用建设页面的,如下图的截图所示。
港口和补给中心可以在盟国和属国的领土上建造。
如果它可以通过车队、其他港口和铁路追踪到首都,那么一个港口将由海上供应,而不需要铁路连接。
补给中心也会要求连接到首都,通过铁路或河流进行追踪。通过河流的连接是即时的,可以考虑是否去造一个新的补给中心(与包含供应中心的省份接壤)连接到首都或链接到另一个补给中心,或港口所在的省份
To connect a new supply hub with a rail connection, open the construction interface and select the “railways” option, and then click on a province with a railway that is connected to the capital, and then click on the province with the new supply hub. The level of the railway constructed will be the same as that of the level of the railway in the province that it’s extending from, but this can be manually adjusted down or up levels (as long as the railway hasn’t been built yet) using either the construction list (the +/- buttons on the railway in the list) or on the supply map (left-click on small number (underneath the crossed hammers) on the railways under construction to increase the level, and right-click to decrease the level).
铁路可以在任何时候在控制、盟友或属国领土内建造,并且不需要等待一个补给中心完成(甚至启动)。
提高基础设施等级
高等级的基础建设也允许补给从补给中心到更远,该流动补给的供应会直线下降,(对于基于5级基础设施而言最大减少至0.3),注意那个基础设施的等级问题是地区链接省份来自流动供应。所以,举个例子,如果这有2个地区,一个地区有5的基础设施和一个边境省份有一个等级1基础设施的地区。会有流动供应,就像5的基础设施流动到1级的基础设施。
与其他扩大供应中心范围的方式一样,随着距离中心(按省)的增加,供应减少的增加意味着任何增加可能只在边缘(即可能增加一个省的范围)。
请注意,每个基础设施的花费是6000CIC--所以诸如等级4的基础设施在一个省份的花费会超过建设一个新的补给中心
火车
为了充分发挥出效率,供应网络需要铁路相连的火车,类似于的要求像海军连接,火车数量的需求与每个补给中心供应需求相关。火车需求在每个补给中心的提示页可以看到.
Train requirements for the network as a whole can be found in the logistics tooltip, which can be brought up by hovering over the logistics icon at the top of the screen (it looks like a crate with a percentage next to it). If there are less trains than the network requires, there will be a reduction in hub supply available to divisions drawing it.
Trains are not subject to attrition, but they can be destroyed by air attack from enemy aircraft using logistical strike.
As well as the base model train, two other train models can be researched over the course of the game. One is an unarmoured “austerity” train – which does the same job as the base model, but at a cheaper price (50 MIC instead of 70). The other is an armoured train, more on which below.
装甲火车
装甲列车是一种特殊类型的列车,更能抵抗敌人的后勤打击空中任务。如果你的库存中有装甲列车,它们将自动比其他类型的火车先使用。装甲列车的生产成本要高得多,为105MIC,因此比初始列车贵得多,是简化列车成本的两倍多。
占领铁路和补给中心
As a front advances into enemy territory, enemy-held rail lines and hubs may come under friendly control. While rail lines may or may not need repairing (rail can be damaged by strategic bombing, or by your opponent using scorched earth before they lose control of the state), they won’t be available for use right away in most situations. When capturing a railroad on territory that is not your core, the cooldown until the railroad can be used is 10 days, while it’s 5 if the territory is a core state, and there is no cooldown if the war is a civil war.
铁路转换时间
一个新占领的补给中心只有在被“转换”铁路连接后才会运行,每个省份要求数天被友军控制才会被连接。然而,对于供应中心,没有转换时间。
天气和地形
天气和地形都对供应系统有影响——天气表和wiki上的地形页面上的表格提供了对不同地形/天气状态的各种供应影响的数据。在考虑地形和天气的影响时,需要注意的事情是:
- 有2个天气因素的影响:
- 供应因素 减少来自供应中心的流动供应(实际上,减少其范围),作为进入一个省的供应流量的百分比减少[待确认]。‘’例如,如果一个地区有深雪的地面条件,而暴风雪-像这样的深冬季天气条件可以在这些天气/地面条件期间大大减少补给的供应范围,那么这些影响就会叠加。
- 补给消耗因素 增加分开使用补给.这两个因素可以依赖特别的环境。
- 有1个地形的影响:
- 流动补给惩罚因素'. This changes the supply fall-off in hub supply when moving away from the hub, and is added to other reductions in supply flow. This isn't a percentage figure, but rather a direct change (usually reduction, but it actually is an increase in urban areas) in the supply amount as it relates to the figures shown for hub supply in the province tooltips.
地区补给
与中心供应不同,地区供应是一个州内提供的固定数量的供应,基于四个点:胜利点、基础设施、人口和所谓的“基础补给”,这是一个地图固定数量的额外供应。来自任何时候人口和基础设施的国家供应将在每个地区(非-无法通行),个别地区没有胜利点,很多地区没有基础供应。
一个地区拥有胜利点会有0.2的地区补给。然后会有0.05的供应了该地区0.05的胜利点(例如,这个地区有1个1点VP,和1个5VP,会有0.5的补给来自VP,生产0.2的基础和0.3的来自该地区6VP)其中的一些示例见下表:
| VP | 50 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 补给供应 | 2.70 | 1.20 | 0.95 | 0.70 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
基础设施提供了每等级提供0.3补给,只要基础建设未受损(基础设施值见下表)——如果是受损,然而一定数量的地区补给的减少直到破损被修复。
| 基础设施等级 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 补给供应 | 1.50 | 1.20 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.30 |
Population adds supply on a diminishing scale from 0.01 supply per province in a state of 30.000 people, to 4.25 supply per province in a state with 23.6 M people. Converted to per 1 million people, the scale slides from 0.3 supply per million sparsely populated states to 0.18 supply per million in very densely populated states (e.g. Chinese states).
State supply is evenly distributed to all the units that are in the state (including air and naval units), before other sources of supply are used. Given this, it’s important to be mindful that while there might be enough state supply to support any units outside of hub range, those units will still have to share that state supply with units drawing supply from hubs or ports.
Understanding state supply is essential to understanding how the supply map mode “heat map” works – as unlike hub supply, the shading of each province on the heat map takes into account that total amount of state supply available for the whole state - but once that state supply is used elsewhere in the state, the available state supply for other provinces is reduced accordingly. Checking an area to see whether the heatmap shading is due to mostly hub or state supply will provide a clearer indication of the effective supply in the province if more forces are moved into the state in other provinces. Please see the example provided by the two screenshots below for a bit more detail.
争议地区
如果一个国家的控制权在两个国家之间相互分裂,国家的供应量将被一分为二。中心、人口和基础设施元素将根据双方所拥有的国家省份的比例进行分配,而来自胜利点的国家供应将提供给任何拥有包含这些胜利点的省份。
空投补给
供应系统的三个支柱中的最后一根是空中供应。空中供应由飞行“空投补给”任务的运输机提供。与国家供应一样,通过此提供的供应总量在飞行空中供应任务的任何省份提供(无论是否在运输机的范围内)。然而,与国家供应不同的是,空气供应是最后抽取的,所以单位只有在不能满足国家和补给中心的全部供应要求时才会利用空中补给。
对于任何空中任务,任务效率将减少可以提供的供应,和效率可以受到一系列元素的影响,包括天气,中队执行任务的供应状态的时候,和空气区的大小之间的关系和中队的范围。在100%的任务效率下,每架供应充足的运输机在良好的天气下飞行,能够提供0.2 每飞机提供.
空气机翼的供应需求是由供应的数量他们能够提供通过他们的任务效率,所以所有其他平等,运输机的翼可以覆盖更大比例的空气区将提供更多的空气供应比相同大小的翼使用不同的机场,给它更少的报道。运输机翼飞行空气供应任务只能使地图和补给中心,不能增加他们自身的空气供应
补给不足的影响
地面单位
The amount of supply a division requires for full supply is based on a range of elements, including the line battalions, the support battalions (logistics battalions reduce overall supply use), weather and the capabilities of their commanders.
If a division is below full supply, a faded or bright red crate icon will appear on its on-map icon, and on its icon in the list of divisions in the army. To get a precise look at a division’s supply status, hover over the icon in the army division list to bring up the tooltip. A division’s supply will move towards the amount that can be supported in the province, whether that’s up or down. So, for example, if a division moves from a province where it is 100% supplied, to one where it is 50% supplied, for the first hour in that new province it will still have 100% supply, and then the division’s supply state will go down as its stored supply runs down to 50%.
There are significant penalties for being out of supply to a range of unit characteristics. Note that there can be a delay between a low supply state being reached and the full penalty kicking in. Unit characteristics impacted by low supply, with the impact increasing as the supply state deteriorates, are:
- Speed
- Max organisation
- Org regain speed
- Attack (with a higher max penalty for units defending (-50%) than units attacking (-20%))
- Breakthrough (for units attacking)
- Defence (for units defending)
- Attrition - if a unit’s level of supply drops to 35% or less, it will begin to take supply-based attrition, increasing the amount of equipment the unit uses by increasing amounts the further supply drops.
Being in a low supply state also has an impact on how quickly manpower reinforcements arrive. As long as a division has a connection to the capital via a continuous path through friendly provinces, ports and/or convoys, manpower reinforcements will arrive - although at very low supply levels they can take a long time. Note, however, that the speed of equipment resupply is not affected by a division’s supply state (but if a division has low supply they will experience constant attrition for as long as this is the case, which may prevent a division from reaching its full equipment levels).
If a division is cut off from the capital, even if it is in full supply due to occupying a victory point or another source of state supply, or due to air supply, it will not receive manpower or equipment reinforcements.
Note that fuel works a bit differently to manpower or equipment. Like manpower and equipment, if a unit is cut-off from their capital, it won’t be replenished. Like manpower, the rate of fuel resupply slows if a unit is not fully supplied. However, unlike manpower, fuel supply stops entirely once the supply state is sufficiently poor. Air supply does not impact fuel supply, so even if a unit can trace a line of provinces to its capital and is fully air supplied, if it doesn’t have enough state or hub supply it may not receive fuel resupply.
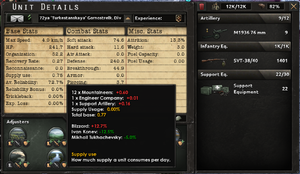
Stored supply/supply grace
Supply grace and stored supply refer to the same thing, which is the amount of supply greater than 100% that will be stored by a division if it is in a fully supplied province. The amount of stored supply for a division can be seen towards the bottom of the tooltip that comes up when hovering over a division’s name in the Army UI element, as per the example below.
The base amount of stored supply that a division can accumulate is 150%. The rate at which it drops varies, but it should enable a division to operate for 2-3 days at full supply efficiency even if the province it is in is not fully supplied, before the stored supply drops below 100%.
For special forces divisions some technologies can increase the length of supply grace. This can be further extended for Marine divisions if they are lead by a general with the “Amphibious”. The extra supply grace provided is described in terms of hours, but this is only broadly indicative, as the rate of reduction in stored supply can vary depending on the situation the division finds itself in.
空中单位
An air unit’s supply is based on the level of supply in the province containing the airbase. If an air unit is flying a mission and is not at 100% supply, it will have a malus on efficiency due to its reduced supply level. It is important to bear in mind that if supply falls below a threshold, the air unit will also not receive enough fuel, reducing mission efficiency even further.
海军单位
For naval units, being less than fully supplied impacts directly on spotting efficiency and repair speed, but it also reduces the rate of fuel received, which depending on the fuel situation can have an impact on their efficiency in combat as well. It is worth bearing in mind that naval units have access to the full amount of potential supply from the hub they're drawing supply from (rather than being limited by what the province can support as well, as per land and air units), so it is far, far less common for naval units to be undersupplied than it is for land or air units.
盟国补给
By default, you can draw supply from your allies’ supply hubs, and your allies can draw supply from your supply hubs. Note, however, that if you’re fighting on allied territory, you can’t use the state supply system. Allied divisions share hub supply with divisions of the host country, but the host country divisions will probably be a bit better supplied as they’ll be able to access whatever state supply is available as well.
While the AI won’t do this, if you want allies not to be involved on a particular front, it’s possible to toggle off supply for allies on a hub-by-hub basis. To toggle supply for allies off (or back on) for a particular hub, click on the hub, and then select the blue flag to the left and above the supply hub symbol (see examples below).