Scopes change the currently-selected entity where the effects should apply or which is checked by the triggers. Each one must follow the same formatting of scope = { <contents> }.
When a scope is used as for effects, each effect inside of the scope's block is executed. Conversely, when a scope is used as for triggers, it serves as a [wp:Logical conjunction logical conjunction], requiring every trigger in the scope's block to be met for that scope to evaluate as true.
In addition to serving as blocks for effects or triggers, some scopes can also serve as targets of effects or triggers: e.g. transfer_state_to = ROOT or owns_state = 123.
However, only some dual scopes can be used as a target. For scopes that cannot be used as targets, PREV, Variables, or Event targets can be used to get around this limitation.
Types
Scopes can be thought of as divided into 3 types by purpose:
- Trigger scopes - those that can only be used in trigger blocks, failing when put within an effect block.
- Effect scopes - those that can only be used in effect blocks, failing when put within an trigger block.
- Dual scopes - those that can be put in both trigger and effect blocks without issues.
It is to be noted that trigger or effect scopes cannot ever be used as targets. That is strictly limited to some dual scopes.
Most of the non-dual scopes follow one of these following patterns:
| Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| all_<name> | Trigger scope, evaluated for each contained scope. Returns false when encountering at least one scope that is false, returns true otherwise. |
| any_<name> | Trigger scope, evaluated for each contained scope. Returns true when encountering at least one scope that is true, returns false otherwise. |
| every_<name> | Effect scope, executes the effects on each contained scope that meets the limit in order. |
| random_<name> | Effect scope, executes the effects on a random contained scope that meets the limit. |
Only some scopes that follow this pattern have equivalents with a different pattern. For example, random_owned_controlled_state exists, but every_owned_controlled_state does not. Each of these non-dual scopes cannot select a country that does not exist, with the exception of every_possible_country.
Additionally, scopes can be divided into 6 types by the targets of the scope for which effects are executed or triggers are checked:
- Country scopes - Executed for countries.
- State scopes - Executed for states.
- Character scopes - Executed for characters. Some subsets exist, such as unit leaders and country leaders.
- Division scopes - Executed for divisions.
- MIO scopes - Executed for military industrial organisations.
- Contract scopes - Executed for purchase contracts.
Only effects or triggers of the same target type can be used. For example, add_building_construction can only be used in a state scope such as random_owned_controlled_state = { ... }, as you can only construct buildings in states. For countries, offsite buildings are used instead.
Examples
Example scope with effects: all contained effects are executed for the scope. This adds 10% ![]() 稳定度 and 20%
稳定度 and 20% ![]() 战争支持度 to the
战争支持度 to the ![]() 苏维埃联盟:
苏维埃联盟:
SOV = {
add_stability = 0.1
add_war_support = 0.2
}Example scope with triggers: all contained triggers must return true for the scope; otherwise, the scope returns false. This requires the state 123 (South-West England) to be owned by the ![]() 联合王国 and controlled by
联合王国 and controlled by ![]() 爱尔兰:
爱尔兰:
123 = {
is_owned_by = ENG
is_controlled_by = IRE
}Example use of PREV as target for non-targetable scope. Since random_country cannot be used as a target, add_to_faction = random_country is not valid syntax; instead, PREV can be used to get around this limitation. The following example adds random country to ROOT's faction:
random_country = {
ROOT = { add_to_faction = PREV }
}
Settings
| File:Ambox outdated info.png | 这部分内容可能已不适合当前版本,最后更新于1.13。 |
Scopes can have additional settings to narrow down the usage. This may change how many and which targets it's able to select or what the tooltip shows.
Limiting
Non-dual scopes that select unit leaders or MIOs, such as every_navy_leader, by default only include those that are visible to the player, i.e. those unit leaders whose roles do not have an unfulfilled visible = { ... } and those MIOs that do not have an unfulfilled visible = { ... }. By including include_invisible = yes, this can be changed. This will look as such:
random_army_leader = {
include_invisible = yes
set_nationality = SWE
}Within only effect scopes, limit = { ... } can be used as a trigger block, evaluated for each possible target contained by the scope. In case of the every_<name> pattern, this will ensure that the tooltip will function properly, which may not be the case when using if directly. In case of the random_<name> pattern, this will remove the possibility of scopes not meeting the triggers being chosen, limiting the selection. For party_leader in specific, the limit must contain has_ideology, while there are no requirements on other scopes. An example of limiting the selection is the following:
every_neighbor_country = { #Targets every neighbor country
limit = { num_of_military_factories > 5 #Limit the scope to neighbor countries with more than 5 (at least 6) military factories } give_military_access = ROOT #Neighbor countries with more than 5 military factories give military access to the ROOT country}
In case of multiple triggers, limit acts like an AND block, requiring each one to be true. To reiterate, this cannot be used within trigger or dual scopes, only in effect scopes.
For scopes of the every_ type, an additional setting for limiting the selection is random_select_amount. In particular, it takes an integer and limits the maximum amount of chosen scopes to that number, picking a random sub-set if exceeded. It is used as such:
every_country = {
random_select_amount = 3 # Selects 3 random countries
country_event = lottery_win.0
}
Tooltip
By default, using a scope of either of the any_, all_, and every_ types will show a title specific to that scope in the tooltip, such as Every country: or All neighbor states:. If scope limits are used, then this changes to the list of scopes that fulfill the limit, such as Corsica, Rome, Sardinia:. For countries, the order in which country tags are created is used in ordering; for states, the state ID is used. If the tooltip differs depending on the scope where it's executed, such as with if statements, then only the first-selected scope is used in the evaluation.
By using tooltip = loc_key within any non-dual scope, including of the random_ type, the tooltip shown to the player can be changed towards the value of the targeted localisation key in the currently enabled language. This will look like the following:
any_country = {
hidden_trigger = {
has_opinion = { target = PREV value > 50 } # Serves as a "limit" hidden from the player.
}
tooltip = any_friendly_country_tt # Replaces "Any country" with the localisation key
has_war_with = ITA
}The localisation key will be defined as such in any localisation file:
l_english: any_friendly_country_tt: "Any friendly country"
This will appear in the tooltip as such:
|
In tooltips of the every_ type where scope limits are used, by default the tooltip unites it into a single scope, such as Germany, United Kingdom, Soviet Union:. By using display_individual_scopes = yes, this will make each selected scope appear in the tooltip separately. For example:
every_neighbor_country = {
limit = {
OR = { has_government = communism has_government = fascism }
}
display_individual_scopes = yes
if = {
limit = {
has_government = fascism
}
add_war_support = -0.1
}
else = { add_stability = -0.1 }
}Without displaying individual scopes, this will be shown as one effect block, such as the following:
|
By the nature of tooltips, the if statements for the first country are evaluated and the same tooltip is shown for both countries. This falsely implies that the Soviet Union will have 10% ![]() 战争支持度 removed. However, adding
战争支持度 removed. However, adding display_individual_scopes = yes changes it to the following:
|
Priority
Within effect scopes of the random_ type, if it is aimed at states, it is possible to prioritize a certain state if possible, by using prioritize as such:
random_owned_controlled_state = {
prioritize = { 123 321 }
limit = {
is_core_of = PREV
}
<...>
}In this case, the limit will first be evaluated for states 123 and 321. Only if neither of the states 123 or 321 meets the conditions of being owned, controlled, and cored by the country will the random_owned_controlled_state scope be able to select a state that isn't 123 or 321. States 123 and 321, in this case, have the same priority: if both have conditions fulfilled, which one will be picked is random. This only applies at scopes of the random_ type which target states, this cannot be done with countries or characters.
Dual scopes
The following scopes can be used either as effect or trigger scopes; some can also be used as the right side of some effects and triggers as a target. If usage as a target is possible, it's marked within the table.
Several dual scopes may have a scope that varies depending on where it's used, such as variables, which can be set to anything.
| Name | Usage | Target type | Example | Description | Usable as target | Version Added |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAG | Always usable | Country scope | SOV = { country_event = my_event.1 }
|
The country defined by the tag or tag alias. Tag aliases are defined in /Hearts of Iron IV/common/country_tag_aliases, as a way to refer to a specific country (such as a side in a civil war) in addition to its actual tag. If the country with the exact tag doesn't exist, but a dynamic country originating from the specified tag does, the scope will refer to the dynamic country. | ✓ | 1.0 |
| <state_id> | Always usable | State scope | 123 = { transfer_state_to = SCO }
|
The state defined by this id. | ✓ | 1.0 |
| <character> | not within Character scope | Character scope | ENG_theodore_makhno = { set_nationality = UKR }
|
On game versions prior to 1.12.8, the character must be already recruited by the country this is scoped from. | ✓ | 1.11 |
| mio:<MIO> | Always usable | MIO scope | mio:AST_cockatoo_doe_organization = { … }
|
The MIO identified by that ID as defined within the /Hearts of Iron IV/common/military_industrial_organization/organizations/*.txt file. | ✓ | 1.13 |
| ROOT | Always usable | Depends on usage | ENG = {
FRA = {
GER = {
declare_war_on = {
target = ROOT
type = annex_everything
}
}
}
} #GER declares war on ENG (if there is no scope before ENG)
|
Targets the root node of the block, an inherent property of each block. Most commonly, this is the default scope: for example, ROOT within a national focus will always refer to the country doing the focus and ROOT within a event will always refer to the country getting the event. However, some blocks do distinguish between the default scope and ROOT, such as certain scripted GUI contexts or certain on actions. If a block doesn't have ROOT defined (such as on_startup in on actions), then it is impossible to use it. | ✓ | 1.0 |
| THIS | Always usable | Depends on usage | set_temp_variable = { target_country = THIS }
|
Targets the current scope where it's used. For example, when used in every_state, it will refer to the state that's currently being evaluated. Primarily useful for variables (as in the example, where omitting it wouldn't work) or for built-in localisation commands, where some scope must be specified. More rarely, this may help with scope manipulation when using PREV. Since omitting it makes no difference in how the code gets interpreted, there is little to no usage outside of these cases. | ✓ | 1.0 |
| PREV | Always usable | Depends on usage | FRA = {
random_country = {
GER = {
declare_war_on = {
target = PREV
type = annex_everything
}
}
}
} #Germany declares war on random_country
|
Targets the scope that the current scope is contained in. Can have additional applications where the assumed default scope differs from the ROOT, such as in state events or some on_actions. Can be chained indefinitely as PREV.PREV. Commonly results in broken-looking tooltips: what's shown to the player doesn't always correlate with reality.
|
✓ | 1.0 |
| FROM | Always usable | Depends on usage | declare_war_on = {
target = FROM
type = annex_everything
}
FROM = {
load_oob = defend_ourselves
}
|
Can be chained indefinitely as FROM.FROM. Used to target various hardcoded scopes inherent to the block, often a secondary scope in addition to ROOT. For example:
In targeted decisions or diplomacy scripted triggers, this refers to the scope that is targeted. |
✓ | 1.0 |
| overlord | Within country scope only | Country scope | overlord = { … }
|
The overlord of the country if it is a subject. Subject to the 'invalid event target' error. | X | 1.3 |
| faction_leader | Within country scope only | Country scope | faction_leader = { add_to_faction = FROM }
|
Faction leader of the faction the country is a part of. Subject to the 'invalid event target' error. | X | 1.10.1 |
| owner | Within state, character, or combatant scope only | Country scope | owner = { add_ideas = owns_this_state }
|
In state scope, the country that owns the state. In combatant scope, the country that owns the divisions. In character scope, the country that has recruited the character. Subject to the 'invalid event target' error when used for a state. | X | 1.0 |
| controller | Within state scope only | Country scope | controller = {
ROOT = {
create_wargoal = {
target = PREV
type = take_state_focus
generator = { 123 }
}
}
}
|
The controller of the current state. Subject to the 'invalid event target' error. | X | 1.0 |
| capital_scope | Within country scope only | State scope | capital_scope = { … }
|
The state where the capital of the current country is located in. Subject to the 'invalid event target' error in rare cases. | X | 1.0 |
| event_target:<event_target_key> | Always usable | Depends on usage | event_target:my_event_target = { … }
|
Saved event target or global event target, with no space after the colon. Subject to the 'invalid event target' error. | ✓ | 1.0 |
| var:<variable> | Always usable | Depends on usage | var:my_variable = { … }add_to_faction = my_variable or
|
Variable set to a scope.
|
✓ | 1.5 |
Invalid event target
- In regards to some dual scopes, a possible logged error to get while using them is "Invalid event target", as in
common/national_focus/generic.txt:690: controller: invalid event target: controller, while the scope being used is not necessarily an event target.
This refers to the scope not having any defined target in the context that it is used, i.e. it is impossible to select any single target when it is used. In case of controller = { ... } as in the example, this means that the scope is checked or executed in a state that isn't controlled by any country. Such states are rather unstable and can cause crashes easily (such as if evaluated for an air mission by AI or if doing almost any effect on them), so if this happens for controller or owner, then this must be fixed only by making sure that every state has an owner or controller.
In practice, this gets skipped over entirely when evaluating the effects or triggers: none of the effects would be executed; as a trigger it'll not come up as either true or false. However, since this can be checked every tick, leaving it as is can result in cluttering the error log. To avoid this, it's possible to use the if statement in effects or triggers in such a manner that the dual scope would only be checked if the conditions for it existing are fulfilled, such as by checking that the country is indeed a subject before checking the overlord. An example of that being done is as such:
if = {
limit = {
is_subject = yes
}
overlord = {
country_event = example.0
}
}While this has identical effects regardless of whether the country is independent or is a subject, this doesn't access the overlord scope for an independent country.
Trigger scopes
These can only be used as triggers; trying to use them as effects will result in nothing happening.
| File:Ambox outdated info.png | 这部分内容可能已不适合当前版本,最后更新于1.13。 |
| Name | Usage | Target type | Example | Description | Version Added |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| all_country | Always usable | Country | all_country = { … }
|
Checks if all countries meet the triggers. | 1.0 |
| any_country | Always usable | Country | any_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country meets the triggers. | 1.0 |
| all_other_country | Within country scope only | Country | all_other_country = { … }
|
Checks if all countries other than the one where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.0 |
| any_other_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_other_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country other than the one where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.0 |
| all_country_with_original_tag | Always usable | Country | all_country_with_original_tag = {
original_tag_to_check = TAG #required
… #triggers to check
}
|
Checks if all countries originating from the specified country, including the dynamic countries created for civil wars and other purposes, meet the triggers. original_tag_to_check = TAG is used to specify the original tag.
|
1.9 |
| any_country_with_original_tag | Always usable | Country | any_country_with_original_tag = {
original_tag_to_check = TAG #required
… #triggers to check
}
|
Checks if any country originating from the specified country, including the dynamic countries created for civil wars and other purposes, meets the triggers. original_tag_to_check = TAG is used to specify the original tag.
|
1.9 |
| all_neighbor_country | Within country scope only | Country | all_neighbor_country = { … }
|
Checks if all countries that border the one where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.0 |
| any_neighbor_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_neighbor_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country that borders the one where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.0 |
| any_home_area_neighbor_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_home_area_neighbor_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country that borders the one where this scope is located, as well as being in its home area - meaning a direct land connection between the capitals of countries - meets the triggers. | 1.0 |
| all_guaranteed_country | Within country scope only | Country | all_guaranteed_country = { … }
|
Checks if all countries that are guaranteed by the one where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.9 |
| any_guaranteed_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_guaranteed_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country that is guaranteed by the one where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.9 |
| all_allied_country | Within country scope only | Country | all_allied_country = { … }
|
Checks if all countries that are allied with the one where this scope is located - meaning that they are either a subject of the country, its overlord, or that they share a faction - meet the triggers. Does not include the country itself. | 1.9 |
| any_allied_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_allied_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country that is allied with the one where this scope is located - meaning that they are either a subject of the country, its overlord, or that they share a faction - meets the triggers. Does not include the country itself. | 1.9 |
| all_occupied_country | Within country scope only | Country | all_occupied_country = { … }
|
Checks if all countries that are occupied by the one where this scope is located - meaning that the occupied country has core states controlled by the occupier country - meet the triggers. | 1.9 |
| any_occupied_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_occupied_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country that is occupied by the one where this scope is located - meaning that the occupied country has core states controlled by the occupier country - meets the triggers. | 1.9 |
| all_enemy_country | Within country scope only | Country | all_enemy_country = { … }
|
Checks if all countries that are at war with the one where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.9 |
| any_enemy_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_enemy_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country that are at war with the one where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.9 |
| all_subject_countries | Within country scope only | Country | all_subject_countries = { … }
|
Checks if all countries that are a subject of the one where this scope is located meet the triggers. Notice the plural spelling in the scope. | 1.11 |
| any_subject_country | Within country scope only | Country | any_subject_country = { … }
|
Checks if any country that is a subject of the one where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.11 |
| any_country_with_core | Within state scope only | Country | any_country_with_core = { … }
|
Checks if any country that has the current scope as a core state meets the triggers. Does not have an equivalent for other effect/trigger scope types. | 1.12 |
| all_state | Always usable | State | all_state = { … }
|
Check if all states meet the triggers. | 1.0 |
| any_state | Always usable | State | any_state = { … }
|
Check if any state meets the triggers. | 1.0 |
| all_neighbor_state | Within state scope only | State | all_neighbor_state = { … }
|
Check if all states that are neighbour to the one where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.0 |
| any_neighbor_state | Within state scope only | State | any_neighbor_state = { … }
|
Check if any state that is neighbour to the one where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.0 |
| all_owned_state | Within country scope only | State | all_owned_state = { … }
|
Check if all states that are owned by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.0 |
| any_owned_state | Within country scope only | State | any_owned_state = { … }
|
Check if any state that is owned by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.0 |
| all_core_state | Within country scope only | State | all_core_state = { … }
|
Check if any state that is cored by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.11 |
| any_core_state | Within country scope only | State | any_core_state = { … }
|
Check if all states that are cored by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.11 |
| all_controlled_state | Within country scope only | State | all_controlled_state = { … }
|
Check if all states that are controlled by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.9 |
| any_controlled_state | Within country scope only | State | any_controlled_state = { … }
|
Check if any state that is controlled by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.9 |
| all_unit_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | all_unit_leader = { … }
|
Checks if all unit leaders (corps commanders, field marshals, admirals) that are employed by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.5 |
| any_unit_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | any_unit_leader = { … }
|
Checks if any unit leader (corps commander, field marshal, admiral) that is employed by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.5 |
| all_army_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | all_army_leader = { … }
|
Checks if all army leaders that are employed by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.5 |
| any_army_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | any_army_leader = { … }
|
Checks if any army leader that is employed by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.5 |
| all_navy_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | all_navy_leader = { … }
|
Checks if all navy leaders that are employed by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.5 |
| any_navy_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | any_navy_leader = { … }
|
Checks if any navy leader that is employed by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.5 |
| all_operative_leader | Within country scope or operations only | Operative | all_operative_leader = { … }
|
Checks if all operatives that are employed by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.9 |
| any_operative_leader | Within country scope or operations only | Operative | any_operative_leader = { … }
|
Checks if any operative that is employed by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.9 |
| all_character | Within country scope only | Character | all_character = { … }
|
Checks if all characters that are recruited by the country where this scope is located meet the triggers. | 1.11 |
| any_character | Within country scope only | Character | any_character = { … }
|
Checks if any character that is recruited by the country where this scope is located meets the triggers. | 1.11 |
| any_country_division | Within country scope only | Division | any_country_division = { … }
|
Checks if any division owned by the current country meets the triggers. | 1.12 |
| any_state_division | Within state scope only | Division | any_state_division = { … }
|
Checks if any division within the current state meets the triggers. | 1.12 |
| all_military_industrial_organization | Within country scope only | MIO | all_military_industrial_organization = { … }
|
Checks if all MIOs within the current country meet the conditions. | 1.13 |
| any_military_industrial_organization | Within country scope only | MIO | any_military_industrial_organization = { … }
|
Checks if any MIO within the current country meets the conditions. | 1.13 |
| all_purchase_contract | Within country scope only | Purchase contract | all_purchase_contract = { … }
|
Checks if all purchase contracts within the current country meet the conditions. | 1.13 |
| any_purchase_contract | Within country scope only | Purchase contract | any_purchase_contract = { … }
|
Checks if any purchase contract within the current country meets the conditions. | 1.13 |
Effect scopes
These can only be used as effects; trying to use them as triggers will result in nothing happening.
| File:Ambox outdated info.png | 这部分内容可能已不适合当前版本,最后更新于1.13。 |
| Name | Usage | Target type | Example | Description | Version Added |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| every_possible_country | Always usable | Country | every_possible_country = { ... }
|
Executes children effects on every country that meets the limit, including those that do not exist. | 1.11 |
| every_country | Always usable | Country | every_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every country that meets the limit. | 1.0 |
| random_country | Always usable | Country | random_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random country that meets the limit. | 1.0 |
| every_other_country | Within country scope only | Country | every_other_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every country that meets the limit and is not the same country as the one this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| random_other_country | Within country scope only | Country | random_other_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random country that meets the limit and is not the same country as the one this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| every_country_with_original_tag | Always usable | Country | every_country_with_original_tag = {
original_tag_to_check = TAG #required
… #effects to run
}
|
Executes contained effects on every country that meets the limit and has the specified original tag. | 1.9 |
| random_country_with_original_tag | Always usable | Country | random_country_with_original_tag = {
original_tag_to_check = TAG #required
… #effects to run
}
|
Executes contained effects on a random country that meets the limit and has the specified original tag. | |
| every_neighbor_country | Within country scope only | Country | every_neighbor_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every country that meets the limit and borders the country this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| random_neighbor_country | Within country scope only | Country | random_neighbor_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random country that meets the limit and borders the country this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| every_occupied_country | Within country scope only | Country | every_occupied_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every country that meets the limit and has any core states controlled by the country this is contained in. | 1.9 |
| random_occupied_country | Within country scope only | Country | random_occupied_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random country that meets the limit and has any core states controlled by the country this is contained in. | 1.9 |
| every_enemy_country | Within country scope only | Country | every_enemy_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every country that meets the limit and is at war with the country this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| random_enemy_country | Within country scope only | Country | random_enemy_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random country that meets the limit and is at war with the country this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| every_subject_country | Within country scope only | Country | every_subject_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every country that meets the limit and is a subject of the country this is contained in. | 1.11 |
| random_subject_country | Within country scope only | Country | random_subject_country = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random country that meets the limit and is a subject of the country this is contained in. | 1.11 |
| every_state | Always usable | State/s | every_state = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every state that meets the limit. | 1.0 |
| random_state | Always usable | State | random_state = {
prioritize = { 123 321 } #optional
… #effects to run
}
|
Executes contained effects on a random state that meets the limit. | 1.0 |
| every_neighbor_state | Within state scope only | State | every_neighbor_state = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every state that meets the limit and neighbours the state this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| random_neighbor_state | Within state scope only | State | random_neighbor_state = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random state that meets the limit and neighbours the state this is contained in. Does not support prioritizing. | 1.0 |
| every_owned_state | Within country scope only | State | every_owned_state = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every state that meets the limit and is owned by the country this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| random_owned_state | Within country scope only | State | random_owned_state = {
prioritize = { 123 321 } #optional
… #effects to run
}
|
Executes contained effects on a random state that meets the limit and is owned by the country this is contained in. | 1.0 |
| every_core_state | Within country scope only | State | every_core_state = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every state that meets the limit and is a core of the country this is contained in. | 1.11 |
| random_core_state | Within country scope only | State | random_core_state = {
prioritize = { 123 321 } #optional
… #effects to run
}
|
Executes contained effects on a random state that meets the limit and is a core of the country this is contained in. | 1.11 |
| every_controlled_state | Within country scope only | State | every_controlled_state = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every state that meets the limit and is controlled by the country this is contained in. | 1.9 |
| random_controlled_state | Within country scope only | State | random_controlled_state = {
prioritize = { 123 321 } #optional
… #effects to run
}
|
Executes contained effects on a random state that meets the limit and is controlled by the country this is contained in. | 1.9 |
| random_owned_controlled_state | Within country scope only | State | random_owned_controlled_state = {
prioritize = { 123 321 } #optional
… #effects to run
}
|
Executes contained effects on a random state that meets the limit and is owned and controlled by the country this is contained in. | 1.3 |
| every_unit_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | every_unit_leader = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every unit leader (corps commanders, field marshals, admirals) that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.5 |
| random_unit_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | random_unit_leader = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random unit leader (corps commanders, field marshals, admirals) that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.5 |
| every_army_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | every_unit_leader = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every army leader that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.5 |
| random_army_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | random_army_leader = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random army leader that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.5 |
| global_every_army_leader | Always usable | Unit Leader | global_every_army_leader = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every army leader that meets the limit. Preferable to use every_army_leader unless necessary to use global_every_army_leader. | 1.5 |
| every_navy_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | every_navy_leader = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every navy leader that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.5 |
| random_navy_leader | Within country scope only | Unit Leader | random_navy_leader = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random navy leader that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.5 |
| every_operative | Within country scope or operations only | Operative | every_operative = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every operative that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.9 |
| random_operative | Within country scope or operations only | Operative | random_operative = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random operative that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.9 |
| every_character | Within country scope only | Character | every_character = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every character that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.11 |
| random_character | Within country scope only | Character | random_character = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random character that meets the limit and is recruited by the country this is contained in. | 1.11 |
| every_country_division | Within country scope only | Division | every_country_division = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every division that meets the limit and is owned by the current country. | 1.12 |
| random_country_division | Within country scope only | Division | random_country_division = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random division that meets the limit and is owned by the current country. | 1.12 |
| every_state_division | Within state scope only | Division | every_state_division = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every division that meets the limit and is located within the current state. | 1.12 |
| random_state_division | Within state scope only | Division | random_state_division = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random division that meets the limit and is located within the current state. | 1.12 |
| every_military_industrial_organization | Within country scope only | MIO | every_military_industrial_organization = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every MIO within the current country that meets the limit. | 1.13 |
| random_military_industrial_organization | Within country scope only | MIO | random_military_industrial_organization = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random MIO within the current country that meets the limit. | 1.13 |
| every_purchase_contract | Within country scope only | Purchase contract | every_purchase_contract = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on every purchase contract within the current country that meets the limit. | 1.13 |
| random_purchase_contract | Within country scope only | Purchase contract | random_state_division = { … }
|
Executes contained effects on a random purchase contract within the current country that meets the limit. | 1.13 |
| party_leader | Within country scope only | Character | party_leader = {
limit = {
has_ideology = liberalism
}
set_nationality = BHR
}
|
Executes the effects on the party leader with the specified ideology type. Must contain a has_ideology in the limit that refers to a specific ideology type (e.g. Despotic), not a group that contain the type (e.g. Non-Aligned). The selected character must be the leader of a party corresponding to the ideology group.
|
1.11 |
NOTE: Some of these scopes may have no countries/states that match the criteria
Effects with scopes
There are the following effects that also change the currently-selected scope:
| Name | Parameters | Examples | Description | Notes | Version Added |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| start_civil_war | ideology = <ideology>The ideology of the breakaway country.
The ruling party of the original, player-led country. Optional.
The size of the breakaway country and the fraction of the original stockpile and military units it will receive by default. Optional, defaults to 0.5.
The size of the land army that the breakaway country gets. Optional, defaults to being the same as size.
The size of the naval forces that the breakaway country gets. Optional, defaults to being the same as size.
The size of the airforce that the breakaway country gets. Optional, defaults to being the same as size.
The capital state of the breakaway country. Optional.
The states included in the breakway country. Optional, defaults to random states based off size.
A trigger block checked for the state that must be met to be transferred to the breakaway. Optional.
List of unit leaders to be kept by their legacy_id. Optional.
Trigger block checked for every unit leader that forces them to be kept if they meet the triggers. Optional.
Controls if the promoted party leader (i.e. the one that'd take power if the country were to be switched to that ideology group) of the revolting ideology group will be kept by the country or join the revolt, yes resulting in the former. Optional, defaults to false.
Controls if non-promoted party leaders of the revolting ideology group will be kept by the country or join the revolt, yes resulting in the former. Optional, defaults to false.
If true, the revolter will have no characters from the original country transferred to them. Optional, defaults to false.
An effect block executed for the breakaway country. |
start_civil_war = {
ruling_party = communism
# Original country's ideology changes to communism
ideology = ROOT
# Breakaway gets old ideology of ROOT
size = 0.8
capital = 282
states = {
282 533 536 555 529 530 528
}
keep_unit_leaders = {
750 751 752
}
keep_political_leader = yes
keep_political_party_members = yes
}
start_civil_war = {
(See country tag aliases)start_civil_war = {
(See usage for PREV and PREV.PREV)
|
Within country scope: starts a civil war for the current scope with the specified parameters, changing the scope to the dynamic country. | states = all would include every single state controlled by the country. If the country's current capital state is set as one of the states that the revolt can gain, it won't fire. set_capital can be used to change the capital beforehand, with On_actions#on_civil_war_end being used to set it back to the default after the civil war ends.
|
1.0 |
| create_dynamic_country | original_tag = <tag>The original tag to be used by the country.
If specified, copies stuff from this tag rather than the original tag.
Effects that will be executed on the new dynamic country. |
create_dynamic_country = {
original_tag = POL
copy_tag = SOV
add_political_power = 100
transfer_state = 123
}
|
Within country scope: Creates a new dynamic country, akin to ones used in civil wars, adding every core of the original tag as core and changing the scope to the dynamic country. | The reserve_dynamic_country effect can be used if the dynamic country does not yet exist in order to ensure that it does not get overwritten by other creations of dynamic countries. | 1.9 |
Array scopes
- 参见:ArraysArrays can be used to create a generic selection of scopes meeting the criteria. These scopes exist for checking conditions on elements of an array or executing effects on them:
| Name | Type | Parameters | Examples | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| any_of_scopes | Trigger | array = <array>The array to check.
The localisation key used for the trigger.
An AND trigger block. |
any_of_scopes = {
array = global.majors
tooltip = has_more_states_than_any_other_major_tt
NOT = { tag = PREV }
check_variable = { num_owned_controlled_states > PREV.num_owned_controlled_states }
}
|
Checks if any value within the array fulfills the triggers, halting and returning true if that's the case, scoping into each element in the array. | Appending _NOT to the tooltip's key (such as has_more_states_than_any_other_major_tt_NOT in the example) results in the localisation key used if this any_of_scopes is put inside of NOT = { ... }.
|
| all_of_scopes | Trigger | array = <array>The array to check.
The localisation key used for the trigger.
An AND trigger block. |
all_of_scopes = {
array = global.majors
tooltip = has_more_states_than_every_other_major_tt
OR = {
tag = PREV
check_variable = { num_owned_controlled_states < PREV.num_owned_controlled_states }
}
}
|
Checks if every value within the array fulfills the triggers, halting and returning false if any one doesn't, scoping into each element in the array. | Appending _NOT to the tooltip's key (such as has_more_states_than_every_other_major_tt_NOT in the example) results in the localisation key used if this any_of_scopes is put inside of NOT = { ... }.
|
| for_each_scope_loop | Effect | array = <array>The array to check.
The temporary variable that can be set to be not 0 to instantly break the loop.
An effect block. |
for_each_scope_loop = {
array = global.majors
if = {
limit = {
NOT = { tag = ROOT }
}
random_owned_controlled_state = {
transfer_state_to = ROOT
}
}
}
|
Runs the effects for every scope within the array. | Equivalent to a every_<...> effect scope type, with additional break.
|
| random_scope_in_array | Effect | array = <array>The array to check.
The temporary variable that can be set to be not 0 to instantly break the loop.
An AND trigger block deciding which scopes can be picked.
An effect block. |
random_scope_in_array = {
array = global.countries
break = break
limit = {
is_dynamic_country = no
exists = no
any_state = {
is_core_of = PREV # Is core of the currently-checked country
}
}
random_core_state = {
transfer_state_to = PREV # Transfers to the currently-selected country.
}
}
|
Runs the effects for a random scope within the array. | Equivalent to a random_<...> effect scope type, with additional break.
|
PREV usage
In order to understand PREV, it can be helpful to think back to the trigger/effect scopes such as every_controlled_state. In this case, if put inside directly, PREV can be used as the controller of the state. In fact, every_controlled_state is equivalent to every_state with a limit of is_controlled_by = PREV in most ways, although it is recommended to use every_controlled_state instead as it is better for optimisation. For example, the following will transfer every state to its controller, changing the owner:
every_country = {
every_controlled_state = {
transfer_state_to = PREV
}
}If thinking of it as a tree, the scopes are in the order of [every_country,every_controlled_state]. Using it within every_controlled_state will refer back to the parent node, or every_country, specifically the country in the every_country list this is currently being executed for. This can be used in other ways, such as obtaining a wargoal against the owner of a state:
123 = {
owner = {
ROOT = {
create_wargoal = {
target = PREV
type = take_state_focus
generator = { 123 }
}
}
}
}In this case, the tree is constructed with [123,owner,ROOT]. Using PREV within ROOT will refer to the previously-defined owner.
Chaining PREV can be done by separating them with a dot as PREV.PREV.PREV. This can be useful if the needed scope is more than 1 scope back.
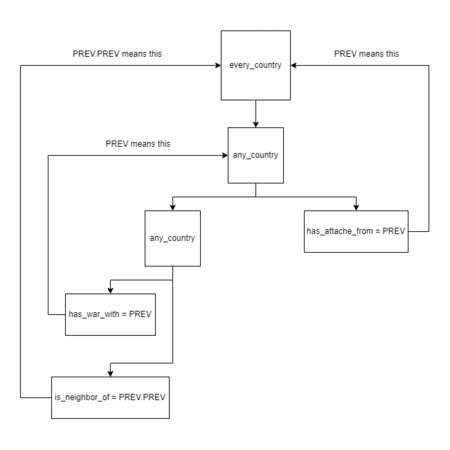
This is an another example of PREV usage with an attached diagram showing how they connect to other scopes:
every_country = {
limit = {
any_country = {
any_country = {
has_war_with = PREV
is_neighbor_of = PREV.PREV
}
has_attache_from = PREV
}
}
country_event = my_event.0
}
In this case, an event will be sent to every country that has sent an attaché to a country that's at war with a neighbour of the original country (i.e. the country that would receive the event). Using PREV.PREV is necessary in this case as all 3 countries don't have single defined tags or pointers and all interact with each other.
In many cases, using PREV can result in seemingly broken tooltips which'll work fine regardless when executing the effects in-game. This typically happens when using it pointing to scopes of the every_<...>/all_<...> types. A single effect or trigger's tooltip can only show one scope as a target at once, and the game would only pick the first possible scope in the tooltip. This can look like the following:
- (Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily):
 瑞士:
瑞士:
- Becomes owner and controller of Sardinia
This can not be avoided with traditional means while still using PREV. Instead, it's possible to use hidden_effect and custom_effect_tooltip or custom_trigger_tooltip in order to completely replace the tooltip in this case.
Flow control tools
While these aren't scopes, not changing where the effects are run or triggers are checked, they still function as blocks of code that can be used within any trigger and/or effect.
| Script | Usage | Example | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AND | Within triggers | AND = {
original_tag = GER
has_stability > 0.5
}
|
Returns false if any sub-trigger returns false, true otherwise. Evaluation stops at the first false sub-trigger.
|
Usually modifies trigger tooltips to include "All of the following must be true" |
| OR | Within triggers | OR = {
original_tag = ENG
original_tag = USA
}
|
Returns true if any sub-trigger returns true, false otherwise. Evaluation stops at the first true sub-trigger.
By default, OR checks each contained trigger separately, AND can be used in order to check between groups of triggers. |
Usually modifies trigger tooltips to include "One of the following must be true" |
| NOT | Within triggers | NOT = {
has_stability > 0.5
has_war_support > 0.5
}
|
Returns false if any sub-trigger returns true, true otherwise. Evaluation stops at the first true sub-trigger.
There is no direct form of logical NAND (true if any contained trigger is false), however |
NOT also allows emulating greater/less than or equals in comparisions that are normally strictly greater or less than.
NOT usually inverts trigger tooltips, though not always predictably or neatly. The inverted tooltip for scopes or |
| count_triggers | Within triggers | count_triggers = {
amount = 2
10 = { state_population_k > 100 }
11 = { state_population_k > 100 }
12 = { state_population_k > 100 }
}
|
Returns true if the number of contained triggers which return true is greater than or equal to the value of amount
|
|
| custom_trigger_tooltip | Within triggers | custom_trigger_tooltip = {
tooltip = sunrise_invasion_tt
any_state = {
is_owned_by = JAP
is_on_continent = europe
is_coastal = yes
}
}
|
Replaces the tooltips from all contained triggers with the custom localisation set by tooltip
|
If the custom_trigger_tooltip is negated (within NOT or a <scripted_trigger> = no, the negated tooltip can be customized by appending _NOT to the localisation key of the tooltip (e.g. sunrise_invasion_tt_NOT).
|
| effect_tooltip | Within effects | effect_tooltip = {
declare_war_on = {
target = FROM
type = annex_everything
}
}
|
Shows the tooltips of the contained effects, but does not execute them. | Most often useful with event chains, where the actual effect is done in a follow-up event. |
| if | Always usable | if = {
limit = {
original_tag = GER
}
has_political_power > 100
}
else_if = {
limit = {
original_tag = ENG
}
has_stability > 0.5
}
else = {
has_war_support > 0.5
}
|
If statements allow to conditionally check triggers or run effects. The limit block is used to define triggers that must be fulfilled for the effects to be run or triggers to be checked. The triggers in limit are never shown to the player: if they are unfulfilled, the if statement will have no tooltip, while, if fulfilled, the player will see the effects/triggers inside the if statement itself.
In addition, |
else_if is optional and can be used as many times as desired. else is also optional, but can only be used once per if.
If statements can be used to clean up tooltips on triggers: the limit can check if the country has a specific tag, while the if statement can contain an always false custom trigger tooltip. This will restrict it from being true for that country, while other countries will not see anything in the tooltip. |
| for_loop_effect | Within effects | for_loop_effect = {
start = -3
end = 9
compare = less_than_or_equals
add = 3
value = value_name
break = break_name
add_political_power = value_name # Adds -3, then 0, then 3, then 6, then 9, after which the loop breaks for 15 total political power.
}
|
Runs the effect in a typical [wp:For_loop for loop], with the current value of the variable kept with the temp variable specified with value. break defines a temp variable that can be set to 1 to break the loop instantly.
|
If unspecified, start and end are 0, compare is less_than, add is 1, value is v, and break is break. Can run for up to 1000 times before stopping automatically.
|
| while_loop_effect | Within effects | while_loop_effect = {
break = temp_break
limit = {
country_exists = GER
}
random_state = {
limit = {
is_owned_by = GER
}
random_country = {
limit = {
NOT = { tag = GER }
}
transfer_state = PREV
}
}
}
|
Runs the effect as long as the trigger is true. break defines a temp variable that can be set to 1 to break the loop instantly.
|
The trigger is checked at the start of each loop only. Can run for up to 1000 times before stopping automatically. If break is unspecified, assumes to be a temp variable with the name of break.
|
| random | Within effects | random = {
chance = 80
add_stability = 0.8
}
|
Simulates a random chance to either execute the effect or do nothing, with the chance used to define the chance.
|
Chance is defined on the scale from 0 to 100. |
| random_list | Within effects | random_list = {
10 = {
modifier = {
factor = 0
has_stability > 0.9
}
add_stability = 0.1
}
20 = {
add_stability = -0.1
}
}
|
Simulates a random chance to pick one of the listed effects. | Chance for each section is proportional, doesn't have to add up to 100. Can use a variable as a chance. Modifiers can be used in the same way as in ai_will_do blocks. |
| 文件 | 效果 • 条件 • 定义 • 修正 • 修正列表 • 作用域 • 本地化 • on action • 数据结构 (标记, 临时标记, 国家别名, 变量, 数组) |
| 脚本 | 成就修改 • AI修改 • AI focuses • 自治领修改 • 权力平衡修改 • 剧本/标签 (游戏规则)• 建筑修改 • 人物修改 • 修饰性TAG修改 • 国家创建 • 军队修改 • 决议制作 • 装备修改 • 事件修改 • Idea修改 • 意识形态修改 • 军工商修改 • 国策制作 • 资源修改 • Scripted GUI • 科技制作 • 单位修改 |
| 地图 | 地图 • 省份 • 补给区域 • 战略区域 |
| 图形图像 | 界面 • 图形资产 • 实体模型 • 后期特效 • 离子效果 • 字体 |
| 装饰性 | 肖像 • 命名列表 • 音乐 • 音效 |
| 其他 | 控制台指令 • 故障排除 • 模组结构 • 成就代码分析 • Mod相关 • Nudger修改 |